欧亚大陆可持续发展目标的空间-时间异质性及其相互作用与关联分析
主题 :Eurasian continent
类型 :Heterogeneity
作者 : Qian Liu Fujia Li Suocheng Dong Hao Cheng Longwu Liang Bing Xia
发布日期 :None
分类 : 社会经济
标签 : Interactions
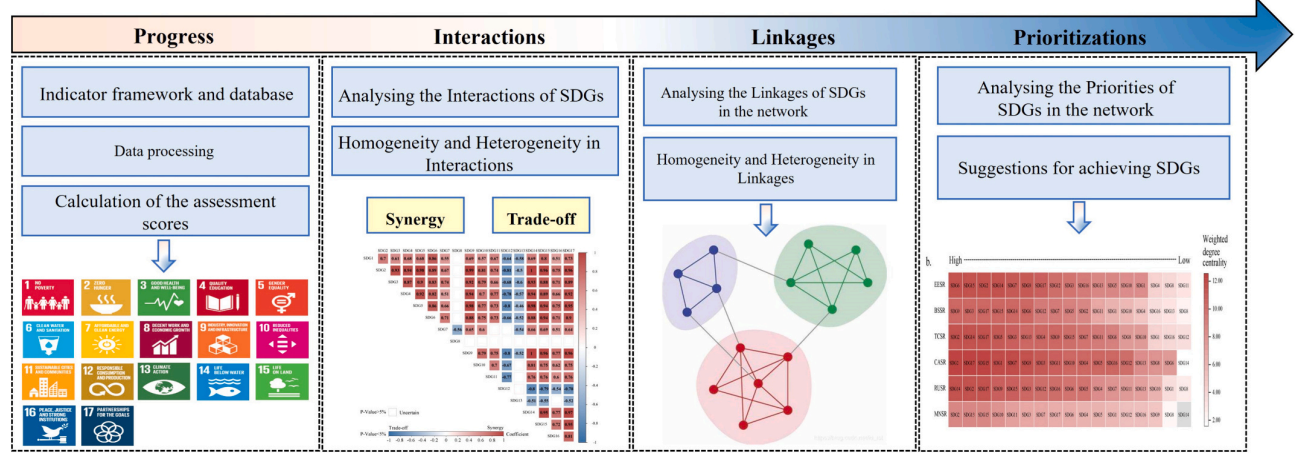
理解可持续发展目标(SDGs)之间的复杂相互作用和联系是优先考虑和推进进展的基础。然而,关于区域尺度可持续发展目标及其相互作用和联系的研究有限。在这里,一种综合方法将允许进步、权衡、协同作用、模块化和优先排序,以揭示不同可持续发展目标之间的关系。然后,从比较区域的角度考虑了同质性和异质性,这意味着我们使用同质性和异质性来分析区域之间的差异。结果表明,欧亚可持续发展目标之间的协同效应大于权衡。权衡集中在可持续发展目标12(负责任的消费和生产)和可持续发展目标13(气候行动)上。至于联系,2000年至2010年期间,欧亚可持续发展目标的模块化从0.2095增加到0.2189,表明模块间联系减弱,模块内联系增强。然而,它在2010年至2020年间趋于稳定。可持续发展目标3(良好健康和福祉)、可持续发展目标4(优质教育)和可持续发展目标1(无贫困)是优先考虑的可持续发展目标。此外,可持续发展目标的进展、相互作用和联系存在空间同质性和异质性。我们的研究强调了空间同质性和异质性,将重点放在具有可持续发展目标进展网络的地区,并可能有助于确定优先事项,以在2030年之前实现尽可能多的可持续发展目标。